DMA Architecture Enhancement Proposal for
Content Based Search
Authors: DMA Query SC: Mitsuru Akizawa,
Yoshifumi Sato, Ann Palmer, Jim Green, Dennis Hamilton, Alan Babich
| HTML Rendition: This HTML rendition was derived from the Microsoft
Word 97 file CBSearch12.doc. It might not be the latest
version of the CBSearch extensions to DMA 1.0. Check the definitive sources for the latest version. There may
be a later packaging of complete, current CBSearch materials there. |
Version 8.0: 6/23/99 Mitsuru Akizawa, Jim Green, Dennis Hamilton, Alan Babich
(CBSearch12.doc) Final (minor) changes before vote. State
that there will be one subclass of the Content Search class for each CBR index supported
by the document space.
Version 7.0: 6/23/99 Mitsuru Akizawa, Jim Green, Dennis Hamilton, Alan Babich
Put in the changes agreed to on the conference call of 5/11/99, and change the data
type of Thesaurus Id from String to Id. Enhance the explanation of the default units for
distance:
Put a sentence in section 3 that states explicitly that the merge rules are not changed
by this proposal.
Add a new class Content Query Options to hold the content based query options. Add a
single object valued property, Content Query Options, to the classes Query and Query
Operator. Do not require support for this property or any of the option properties, and do
not require a default value for any of the options.
The use of thesauri is on a best effort basis. The query will be executed, and no error
will be returned, even if a thesaurus is not available.
In the introduction it is noted that there can be multiple instances of the Result
Object property in the Selections list.
Put in an example showing the use of the Result Object property.
Version 6.0: 4/27/99 Mitsuru Akizawa, Jim Green, Dennis Hamilton, Alan Babich
Change the name of the Proximity operator to Within. Add new query operators NotWithin,
WithinUnits, NotWithinUnits. Add HitCount property.
Version 5.0: 4/4/99 Mitsuru Akizawa, Jim Green, Dennis Hamilton, Alan Babich
Add example query trees. Explain how to take advantage of the new properties in the
Query class. Get rid of the Word macros. Use the value 1 to indicate adjacency instead of
0. This change anticipates that an operand will be added to the Proximity operator to
specify the units of . For example, if the units were specified to be
"paragraph", then 0 would mean that the search terms must be in the same
paragraph, and 1 would mean that the search terms must be in adjacent paragraphs. The old
way, -1 would have to be used to indicate that the search terms are in the same paragraph.
Version 4.0: 2/16/99 Mitsuru Akizawa, Yoshifumi Sato, Ann Palmer, Jim Green,
Dennis Hamilton, Alan Babich
Touch up the wording in the overview.
Changed the options from list of Booleans to separate properties.
Wrote the query overview.
Dropped the last Editor’s note.
Version 3.0: 1/19/99 Mitsuru Akizawa, Yoshifumi Sato, Ann Palmer, Jim Green,
Alan Babich
Added a paragraph on the scope of the proposal in the introduction.
Clarified the confusion between class and class instance in the introduction.
Added Content Search to the glossary of terms.
Explained that the relative importance of two retrieval terms in a query is indicated
by the ratio of their retrieval term weights.
Changed the data type of Raw Score, Normalized Score, and weights from integer32 to
float64.
Moved the Special Properties to another proposal.
Made the list of options be list of integer32, not list of Boolean. Added format level
"option".
Provided new name (DMA_CBR_OPTION_SPELLING_VARIANT) and new description for
DMA_CBR_OPTION_TRANSLATION_EXPANSION.
Made Thesaurus name a list of strings, and enhanced its description.
Deleted the Contains SGML and SGML operators.
Rewrote the sentence on internationalization considerations.
Removed most editor’s notes.
Minor wording touch ups.
Version 2.0: 12/10/98 Mitsuru Akizawa, Yoshifumi Sato, Ann Palmer, Jim Green,
Alan Babich
Added operator for searches of SGML, HTML, and XML documents. Correct the statement
that the Hitachi proposal is based on STARTS. It is not. It used the concept of raw and
normalized score, however. Corrected some minor errors in the document.
Version 1.0: 12/06/98 Mitsuru Akizawa, Yoshifumi Sato, Ann Palmer, Jim Green,
Alan Babich
Initial version.
New/Changed Interfaces
Integration Model
Content
Containment
Versioning
Security
Naming
Performance Impact
Failure Modes/Crash Recovery
The scope of this proposal is to define a small, basic, interoperable subset of content
search that is to be added to the DMA API. The intent is to enable DMA query to provide
access to basic content search capability, assuming that is provided by the document space
implementation. This proposal is not intended to allow access to every feature of every
search engine that currently exists.
A new class is added to the DMA classes – Content Search.
It is expected that the Content Search class will be supported and have exactly one
subclass for each CBR index supported by the document space. It is possible for each
content index to be managed by different content search engine software."
A query against the Content Search class (or one of its subclasses) implies a query
against the corresponding content index.
It should be noted that documents of many different types are typically indexed in the
same content index. It is also possible to include folders and annotations in the content
index. Therefore, searches against the Content Search class can in effect search across
multiple different subclasses of DocVersion and possibly other classes as well.
The properties of an instance of Content Search reflect properties stored in the
corresponding content index. A new object valued property, Result Object, is introduced as
a property of the new Content Search class. The act of accessing the value of the Result
Object property of a query result row causes a connected scratch pad object for the
DocVersion or other object associated with the result row to be instantiated on the
client. Note that there can be multiple instances of the Result Object property in the
Selections list.
The Content Search class is intended to be a virtual class: The Content Search class is
intended for use only in queries. No provision is made for inserting, updating, or
deleting independently persistable objects of an instance of the Content Search class via
the DMA API. Indexing and deindexing of documents in a content index is expected to be
done out of band of the DMA API.
New "score" properties of the Content Search class that allow the results of
content based queries to be ranked in descending order of relevance are defined in this
proposal.
In addition to the new Content Search class, new query operators that perform various
types of content based search operations are defined in this proposal.
This proposal does not propose any changes to the merge rules for constructing merged
scopes.
This proposal is based on a working paper submitted by Mr. Mitsuru Akizawa and Mr.
Yoshifumi Sato of Hitachi, as modified by the subsequent discussions of the DMA Query
subcommittee.
Content search is querying for documents by specifying conditions on the document
content. Typically, the documents involved are parsed by special document indexing
software, and indexed in a content index. The entries in the content index refer back to
the original documents.
Retrieval Term
A retrieval term is word or phrase looked up in a content index by content based
retrieval (CBR) software.
Retrieval Term Weight
If there are multiple retrieval terms in a content based query, it may be desirable
to indicate the relative importance of each term to the query. That is done by assigning a
weight to each retrieval term. The retrieval term weight is a real number between 0.0 and
1.0 . The ratio of two retrieval term weights indicates the relative importance of the two
retrieval terms. Retrieval term weights are not normalized. That is, there is no
requirement that the sum of the retrieval term weights adds up to 1.0 or any other number.
Raw Score, Normalized Score
The raw score is intended to be useful for ranking purposes when a single content
based index is involved in a query. In some document spaces, the raw score is based on the
number of occurrences of the search terms in the document, and on other statistics (e.g.
the number of documents in the content index that contain the search term, the total
number of documents in the content index, etc.). When multiple content indexes are
involved in a query, the raw scores are typically not directly comparable, even if the
same scoring algorithm is used. That is because the raw score of a document for a
particular query typically depends upon all the documents in the content index. Therefore,
when multiple content indexes are involved in a query, the normalized score is generally
used for ranking purposes. The normalized score may not be perfectly comparable across
content based indexes, but it is generally much more appropriate than the raw score in
such cases.
This is a new, virtual class. Objects of this class can not be created, deleted,
modified, or connected to in the usual way. It is intended that the primary use of this
class be in content based queries.
Adding and deleting objects of this class is outside of the scope of this proposal. The
Name property is not assigned. This class must be searchable but not addressable or
navigable.
Class ID: dmaClass_ContentSearch
Superclass: DMA
Interfaces
The interfaces are inherited from the superclass DMA. These are IUnknown,
IdmaObject, and IdmaProperties. However, objects of this class can not be instantiated.
This class exists to provide properties that can be selected in a query result set.
Properties
| Name |
Impl. Req'd |
System Gen'ed |
Read-Only |
Value Req'd |
Type |
Cardinality |
Req'd Class |
| OIID |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
String |
Scalar |
|
| Class Description |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Object |
Scalar |
Class Description |
| This |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Object |
Scalar |
Content Search |
| Create Pending |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Boolean |
Scalar |
|
| Update Pending |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Boolean |
Scalar |
|
| Delete Pending |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Boolean |
Scalar |
|
| Content |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
String |
Scalar |
|
| Result Object |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
object |
Scalar |
DMA |
| Raw Score |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Float64 |
Scalar |
|
| Normalized Score |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Float64 |
Scalar |
|
| Document Length |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Integer32 |
Scalar |
|
| Hit Count |
- |
Yes |
Yes |
- |
Integer32 |
Scalar |
|
Detailed Description
It is useful to think of the persistent data associated with an instance of the
Content Search class (or one of its subclasses) as a content index.
The properties of an instance of the Content Search class reflect the properties stored
in the corresponding content index.
The Content Search class and its subclasses must be searchable. Searches against it
correspond to searches against a content index.
The primary use of this class is to facilitate content queries. It is not intended that
it be possible to connect scratchpad objects for members of this class or to create new
persistent members of this class (e.g., via the ExecuteChange method). The intent is that
indexing and deindexing of documents or other objects in the content index is done out of
band with respect to the DMA API.
Search results from this class correspond to documents or other objects indexed in the
content based index. A connected scratchpad object for the document or other object
associated with a result row may be obtained by accessing the value of the Result Object
property.
It is expected that if a document space has more than one content index, then there
will be an instance of Content Search or one of its subclasses for each such content index
in that document space. Different search engine software can be used to manage each
content index.
Property Descriptions
• OIID {dmaProp_OIID}
Property Inherited from DMA
This property may not be implemented.
• Class Description {dmaProp_ClassDescription}
Property Inherited from DMA
This property may not be implemented.
• This {dmaProp_This}
Property Inherited from DMA
This property may not not be implemented.
• Create Pending {dmaProp_CreatePending}
Property Inherited from DMA
This property may not be implemented.
• Update Pending {dmaProp_UpdatePending}
Property Inherited from DMA
This property may not be implemented.
• Delete Pending {dmaProp_DeletePending}
Property Inherited from DMA
This property may not be implemented.
• Content {dmaProp_Content}
This property stands for the content of the document or other target object. This
property is merely a placeholder needed by content search query operators. (Query
operators need an operand that designates the property being queried.) There must be no
value for this property (the content must be obtained by accessing the Result Object
property and then using the usual DMA 1.0 methods to access its content).
• Result Object {dmaProp_ResultObject}
This object-valued property references the actual document or other object that
corresponds to a query result row of a search against the Content Search class (or one of
its subclasses). In order to obtain a scratchpad object for the target object, this
property is mentioned in the Selections list property of the query, and its value is
retrieved from a result row of the query.
• Raw Score {dmaProp_RawScore}
The value of this property is the raw score of the document, i.e., this score value is
not normalized. The value of this property can be used to order the documents retrieved by
a content query in order of decreasing relevance. The Raw Score is most useful when the
query is against a single document space. The Raw Score property values are not comparable
across document spaces: The values of Raw Score of the same document stored in two
different document spaces may be different.
• Normalized Score {dmaProp_NormalizedScore}
The value of this property is the normalized score of the document. The Normalized
Score can be used to order the documents retrieved by a content query in order of
decreasing relevance. The Normalized Score is expected to be more useful than the Raw
Score when the query is across multiple document spaces. However, although using the
Normalized Score is better than using the Raw Score in the case of multiple document
spaces, there is no guarantee that the normalized scores from different document spaces
will be perfectly comparable.
• Document Length {dmaProp_DocumentLength}
This is the length in bytes of the rendition of the document that was indexed in the
content index. This property is optionally supported.
• Hit Count {dmaProp_HitCount}
For the case that there is a single Contains operator, the value of this property is
the number of occurrences of the search term in the document associated with the Result
Object property. For other cases, the value of Hit Count is implementation defined. This
property might be null for some content queries and non null for others.
Other Properties in the Content Based Index
It is usually the case that content search engines support the indexing of
"hard" properties of documents (e.g., "Author", "Title",
"LoanNumber", etc.) in addition to document content. To make such
"hard" properties searchable or retrievable from the content based index, they
must be properties of Content Search or a subclass of Content Search. If any of the hard
properties are strings, they can be used as the target property for the content search
query operators if the document space implementation supports that. The normal query
operators (e.g., dmaQueryOperaor_GreaterInteger32, etc.) can also be used against the hard
properties in the content index.
This class is added to collect the options that may apply to a content based query.
It’s immediate superclass is Query Node.
The following are the properties introduced by this class:
Properties
| Name |
Impl. Req'd |
System Gen'ed |
Read-Only |
Value Req'd |
Type |
Cardinality |
Req'd Class |
| CBR Soundex |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Boolean |
|
|
| CBR Stemming |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Boolean |
|
|
| CBR Thesaurus |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Boolean |
|
|
| CBR Right Truncation |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Boolean |
|
|
| CBR Left Truncation |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Boolean |
|
|
| CBR Case Sensitive |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Boolean |
|
|
| CBR Spelling Variant |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Boolean |
|
|
| Thesaurus Names |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Id |
list |
|
Property Descriptions
• CBR Soundex {dmaProp_CBRSoundex}
If CBR Soundex is set, then the search is based on soundex values, not the word itself.
Otherwise, soundex values are not used in the search.
• CBR Stemming {dmaProp_CBRStemming}
If CBR Stemming is set, then stemming is applied to search terms. Otherwise, stemming
is not performed.
• CBR Thesarus {dmaProp_CBRThesaurus}
If CBR Thesaurus is set, then thesaurus expansion is applied to search terms.
Otherwise, thesaurus expansion is not performed. (See the Thesaurus Names property of the
Query class.)
• CBR Right Truncation {dmaProp_CBRRightTruncation}
If CBR Right Truncation is set, then search terms are truncated on the right end to
remove any ending or suffix before being looked up in the content based index. Otherwise,
right truncation is not performed.
• CBR Left Truncation {dmaProp_CBRLeftTruncation}
If CBR Left Truncation is set, then search terms are truncated on the left end to
remove any prefix before being looked up in the content based index. Otherwise, left
truncation is not performed.
• CBR Case Sensitive {dmaProp_CBRRightTruncation}
If CBR Case Sensitive is set, then, the lookup in the content based index is sensitive
to case. Otherwise, the lookup is case insensitive.
• CBR Spelling Variant {dmaProp_CBRSpellingVariant}
If CBR Spelling Variant is set, then spelling variant expansion is applied to search
terms before they are looked up. Otherwise, spelling variant expansion is not applied.
Spelling variant expansion means searching for the retrieval term or any of its
alternative spellings. The expansion strongly depends on language or locale. Spelling
variant expansion is different from synonym expansion (see the CBR Thesaurus property),
because the alternative spelling of the retrieval term is semantically identical to the
original retrieval term, not a synonym for it.
For example, consider Katakana. Katakana uses phonograms. Katakana is used in Japanese
documents to denote foreign words, e.g., "computer", based on how they sound. It
is often hard to decide accurately what the sound of a foreign word is, due to differences
in pronunciation of the foreign word. As a result, there can be several commonly used
Katakana spellings of a foreign word.
As another example, the spelling expansion for "color" might include
"colour" in English documents.
• Thesaurus Names {dmaProp_ThesaurusNames}
This property specifies a list of names of thesauri, one of which is to be used for the
content search, if available. A document space may or may not use a thesaurus during
content search, and, even if it does, it may or may not allow a thesaurus other than the
default to be specified. Specification of thesauri is a hint, not an absolute requirement.
In other words, the query will be attempted in all relevant document spaces whether or not
the specified thesaurus is available in any particular document space. No error indication
will be given if the specified thesaurus is not available in a document space.
If the query option CBR Thesaurus is not set, a document space may use its default
thesaurus if it has one, or may choose to not use a thesaurus.
Assume that CBR Thesaurus is set. Then the following things are true:
- If Thesaurus Names has zero elements, the document space’s default thesaurus will
be used, if there is one.
- If Thesaurus Names has one or more elements, then the first (i.e., lowest list index)
thesaurus name that the document space implementation recognizes will be used. If none are
recognized by the document space implementation, the document space implementation will
use its default thesaurus, if it has one.
The following new property is added to this class: dmaProp_ContentQueryOptions.
| Name |
Impl. Req'd |
System Gen'ed |
Read-Only |
Value Req'd |
Type |
Cardinality |
Req'd Class |
| Content Query Options |
- |
- |
- |
- |
Object |
|
Content Query Options |
Note that the name of this property is the same as the name of its required class.
If this property has a value, then the values of its properties (i.e., CBR Soundex, CBR
Stemming, etc.) specify global content search options that are apply to all the content
based retrieval operators in the current query. These global options may possibly be
overridden on an operator-by-operator basis by the value of this same property in a query
operator instance in the query.
The Content Query Options property is to be added to the Query Operator class (as well
as the Query class). The values of the properties in this occurrence of the Content Query
Options property override the global options specified by this same property on the
instance of Query class, if any. This provides a mechanism to override the global search
options specified on the Query object on an operator-by-operator basis.
If content search is not supported, the Content Query Options property is not
supported. It is not required that the property be supported on the Query Operator class,
even if the property is supported on the Query class.
N/A
The query model is not affected by this proposal. However, new operators must be
defined to provide content search functionality.
The companion proposal defining capabilities for content search query will indicate
whether or not there are some constraints on the form of query expressions. A fully
general query would include conditions on properties of the Content Search class as well
as other classes, and that would require more effort than an implementation that allowed
queries against only properties of Content Search, or properties not of Content Search.
The query model overview should be updated by adding the following section to the DMA
1.0 specification to the very end of the query overview as section 3.5.14 "Content
Based Search":
The Content Search class exists to support content searches.
The Content Search class is intended to be a virtual class: The Content Search class is
intended for use only in queries. No provision is made for inserting, updating, or
deleting independently persistable objects of an instance of the Content Search class via
the DMA API. Indexing and deindexing of documents in a content index is expected to be
done out of band of the DMA API.
It is expected that the Content Search class will be supported and have exactly one
subclass for each CBR index supported by the document space. It is possible for each
content index to be managed by different content search engine software."
A query against the Content Search class (or one of its subclasses) implies a query
against the corresponding content index.
It should be noted that documents of many different types are typically indexed in the
same content index. It is also possible to include folders and annotations in the content
index. Therefore, searches against the Content Search class can in effect search across
multiple different subclasses of DocVersion and possibly other classes as well.
The properties of an instance of Content Search reflect properties stored in the
corresponding content index. The object valued property, Result Object, is a property of
the new Content Search class. The act of accessing the value of the Result Object property
of a query result row causes a connected scratch pad object for the DocVersion or other
object associated with the result row to be instantiated on the client.
The "score" properties of the Content Search class that allow the results of
content based queries to be ranked in descending order of relevance. (See "raw score,
normalized score" in the glossary. See also "content search",
"retrieval term", and "retrieval term weight".)
Query operators, such as Contains and Within, are specialized for content based
searching.
Content search options global to the query are specified by certain property values of
the Content Query Options property of the Query object (e.g., CBR Soundex, CBR Case
Sensitive, etc.). These global settings may be overridden for a sub part of the query by
values for these same properties of the Content Query Options property on certain Query
Operator objects, e.g. those with Query Operator Id equal to dmaQueryOperator_Contains or
dmaQueryOperator_Within.
| Name |
Result Type |
Min # of Opnds |
Max # of Opnds |
Operand Type(s) |
Safe to Eliminate |
Define |
| Contains |
Boolean |
3 |
3 |
0: object (class is Query Property) 1: string
2: float64 |
Yes |
dmaQueryOperator_Contains |
dmaQueryOperator_Contains
This operator returns DMA_TRUE if and only if the content of the document referred
to by the current object under scan in the content index contains the retrieval terms
specified in the operands. Otherwise, it returns DMA_FALSE.
Operand 0 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Property. The
Searchable Class Occurrence must designate the Content Search class or one of its
subclasses. The Property Id usually designates the Content property of Content Search.
Operand 1 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be looked
up in the content index).
Operand 2 is of class Query Constant Float64 specifying the retrieval term weight. The
weight must be between 0.0 and 1.0 . (The ratio of two weights indicates the relative
importance of two retrieval terms or co-occurrences.)
| Name |
Result Type |
Min # of Opnds |
Max # of Opnds |
Operand Type(s) |
Safe to Eliminate |
Define |
| Within |
Boolean |
6 |
6 |
0: object (class is Query Property) 1: String
2: String
3: integer32
4: Boolean
5: float64 |
Yes |
DmaQueryOperator_Within |
dmaQueryOperator_Within
This operator is useful to find documents in which two search terms (i.e., words or
phrases) occur near each other. Specifically, this operator returns DMA_TRUE if and only
if all of the following conditions are satisfied: (1) the content of the document referred
to by the current object under scan in the content index contains both of the two
retrieval terms specified in the operands, and (2) the distance between the two terms in
the co-occurrence must be less than or equal to a specified distance of each other, and,
(3) if it matters which retrieval term occurs first, then when a co-occurrence of both
retrieval terms satisfies the proximity condition, the first retrieval term does indeed
occur before the second retrieval term. Otherwise, the operator returns DMA_FALSE.
Operand 0 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Property. The
Searchable Class Occurrence must designate the Content Search class or one of its
subclasses. The Property Id usually designates the Content property of Content Search.
Operand 1 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the first retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be
looked up in the content index).
Operand 2 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the second retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be
looked up in the content index).
Operand 3 is of class Query Constant Integer32. The value indicates the maximum
distance allowed between the occurrence of the retrieval terms of operand 1 and operand 2
in the document. A value of 1 indicates adjacency. A value of 2 indicates at most one
intervening thing, etc. The units of distance for this operator are the, so called, default
units. (See the description of DMA_DISTANCE_DEFAULT in the Within Units operator.) For
most languages, the default units are words. For some Asian languages, the default units
are characters, because the concept of "word" is not applicable. For example, if
operand 3 had the value 1, then the search term of operand 1 must be adjacent to the
search term of operand 2.
Operand 4 is of class Query Constant Boolean. If the value is DMA_TRUE, then the first
search term must occur first. If the value is DMA_FALSE, then either the first or the
second search term may occur first, and the other search term must occur next.
Operand 5 is of class Query Constant Float64. The value specifies the weight for the
co-occurrence of the two retrieval terms. The weight must be between 0.0 and 1.0 . (The
ratio of two weights indicates the relative importance of the two retrieval terms or
co-occurrences.)
| Name |
Result Type |
Min # of Opnds |
Max # of Opnds |
Operand Type(s) |
Safe to Eliminate |
Define |
| NotWithin |
Boolean |
6 |
6 |
0: object (class is Query Property) 1: String
2: String
3: integer32
4: Boolean
5: float64 |
Yes |
DmaQueryOperator_NotWithin |
dmaQueryOperator_NotWithin
This operator is useful to find documents in which two search terms (i.e., words or
phrases) occur near each other. Specifically, this operator returns DMA_TRUE if and only
if all of the following conditions are satisfied: (1) the content of the document referred
to by the current object under scan in the content index contains both of the two
retrieval terms specified in the operands, and (2) the two terms in the co-occurrence are
greater than a specified distance from each other, and, (3) if it matters which retrieval
term occurs first, then when a co-occurrence of both retrieval terms satisfies the
proximity condition, the first retrieval term does indeed occur before the second
retrieval term. Otherwise, the operator returns DMA_FALSE.
Operand 0 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Property. The
Searchable Class Occurrence must designate the Content Search class or one of its
subclasses. The Property Id usually designates the Content property of Content Search.
Operand 1 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the first retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be
looked up in the content index).
Operand 2 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the second retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be
looked up in the content index).
Operand 3 is of class Query Constant Integer32. The value is one less than the minimum
distance allowed between the occurrence of the retrieval terms of operand 1 and operand 2
in the document. A value of 1 indicates adjacency. A value of 2 indicates at most one
intervening thing, etc. The units of distance for this operator are the, so called, default
units. (See the description of DMA_DISTANCE_DEFAULT in the Within Units operator.) For
most languages, the default units are words. For some Asian languages, the default units
are characters, because the concept of "word" is not applicable. For example, in
English documents, if operand 3 had the value 1, then the search term of operand 1 must be
have at least one intervening word between it and the search term of operand 2.
Operand 4 is of class Query Constant Boolean. If the value is DMA_TRUE, then the first
search term must occur first. If the value is DMA_FALSE, then either the first or the
second search term may occur first, and the other search term must occur next.
Operand 5 is of class Query Constant Float64. The value specifies the weight for the
co-occurrence of the two retrieval terms. The weight must be between 0.0 and 1.0 . (The
ratio of two weights indicates the relative importance of the two retrieval terms or
co-occurrences.)
| Name |
Result Type |
Min # of Opnds |
Max # of Opnds |
Operand Type(s) |
Safe to Eliminate |
Define |
| Within Units |
Boolean |
7 |
7 |
0: object (class is Query Property) 1: String
2: String
3: integer32
4: Boolean
5: float64
6: integer32 |
Yes |
DmaQueryOperator_WithinUnits |
dmaQueryOperator_WithinUnits
This operator is useful to find documents in which two search terms (i.e., words or
phrases) occur near each other. This operator differs from the Within operator by the
addition of an operand specifying the units of the distance metric. Specifically, this
operator returns DMA_TRUE if and only if all of the following conditions are satisfied:
(1) the content of the document referred to by the current object under scan in the
content index contains both of the two retrieval terms specified in the operands, and (2)
the distance between the two terms in the co-occurrence must be less than or equal to a
specified distance of each other, and, (3) if it matters which retrieval term occurs
first, then when a co-occurrence of both retrieval terms satisfies the proximity
condition, the first retrieval term does indeed occur before the second retrieval term.
Otherwise, the operator returns DMA_FALSE.
Operand 0 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Property. The
Searchable Class Occurrence must designate the Content Search class or one of its
subclasses. The Property Id usually designates the Content property of Content Search.
Operand 1 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the first retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be
looked up in the content index).
Operand 2 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the second retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be
looked up in the content index).
Operand 3 is of class Query Constant Integer32. The value indicates the maximum
distance allowed between the occurrence of the retrieval terms of operand 1 and operand 2
in the document.
Operand 4 is of class Query Constant Boolean. If the value is DMA_TRUE, then the first
search term must occur first. If the value is DMA_FALSE, then either the first or the
second search term may occur first, and the other search term must occur next.
Operand 5 is of class Query Constant Float64. The value specifies the weight for the
co-occurrence of the two retrieval terms. The weight must be between 0.0 and 1.0 . (The
ratio of two weights indicates the relative importance of the two retrieval terms or
co-occurrences.)
Operand 6 indicates the distance metric to be used. The following macros in the DMA
header files for C and C++ evaluate to small integer constants and can be used to specify
the distance metric:
• DMA_DISTANCE_DEFAULT
- The default units are words for most languages, and characters for some Asian languages,
because the concept of "word" is not applicable. For documents containing text
from multiple languages, the default units may be different in different parts of the
document, depending upon the language of those parts. For example, suppose a Japanese
document includes some quotations in English. Assume the Japanese parts of the document in
Japanese are in a Japanese character set such that the default units are Japanese
characters. The default units for the parts of the document in English would be words.
• DMA_DISTANCE_CHARACTERS
Units of Character means characters in all languages.
• DMA_DISTANCE_WORDS
This metric indicates words. The Words distance metric does not apply to some Asian
languages.
• DMA_DISTANCE_SENTENCES
This metric indicates sentences.
• DMA_DISTANCE_PARAGRAPHS
This metric indicates paragraphs.
Search terms are words or phrases. A value of one for the distance operand of the
Within, NotWithin, WithinUnits, and NotWithinUnits operators indicates adjacent search
terms. In the case of a distance metric that is normally composed of more than one word
(e.g., DMA_DISTANCE_SENTENCES and DMA_DISTANCE_PARAGRAPHS), a value of zero means
"within the same paragraph (or sentence, etc.)."
| Name |
Result Type |
Min # of Opnds |
Max # of Opnds |
Operand Type(s) |
Safe to Eliminate |
Define |
| Not Within Units |
Boolean |
7 |
7 |
0: object (class is Query Property) 1: String
2: String
3: integer32
4: Boolean
5: float64
6: integer32 |
Yes |
DmaQueryOperator_NotWithinUnits |
dmaQueryOperator_NotWithinUnits
This operator is useful to find documents in which two search terms (i.e., words or
phrases) occur near each other. The difference between this operator and the NotWithin
operator is that there is an additional operand specifying the distance metric.
Specifically, this operator returns DMA_TRUE if and only if all of the following
conditions are satisfied: (1) the content of the document referred to by the current
object under scan in the content index contains both of the two retrieval terms specified
in the operands, and (2) the two terms in the co-occurrence are greater than a specified
distance from each other, and, (3) if it matters which retrieval term occurs first, then
when a co-occurrence of both retrieval terms satisfies the proximity condition, the first
retrieval term does indeed occur before the second retrieval term. Otherwise, the operator
returns DMA_FALSE.
Operand 0 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Property. The
Searchable Class Occurrence must designate the Content Search class or one of its
subclasses. The Property Id usually designates the Content property of Content Search.
Operand 1 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the first retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be
looked up in the content index).
Operand 2 is a scalar object valued property that must be of class Query Constant
String. The value of the string is the second retrieval term (i.e., a word or phrase to be
looked up in the content index).
Operand 3 is of class Query Constant Integer32. The value is one less than the minimum
distance allowed between the occurrence of the retrieval terms of operand 1 and operand 2
in the document.
Operand 4 is of class Query Constant Boolean. If the value is DMA_TRUE, then the first
search term must occur first. If the value is DMA_FALSE, then either the first or the
second search term may occur first, and the other search term must occur next.
Operand 5 is of class Query Constant Float64. The value specifies the weight for the
co-occurrence of the two retrieval terms. The weight must be between 0.0 and 1.0 . (The
ratio of two weights indicates the relative importance of the two retrieval terms or
co-occurrences.)
Operand 6 specifies the distance metric, exactly the same as in the WithinUnits
operator.
When querying textual content, the word equality algorithms specific to the language
and locale of the document must be used.
Suppose you wanted to find documents that contained the phrase "stock market
crash", and the relative importance of this retrieval term is 1.0. Then you could
have the following query subtree in the query parse tree:
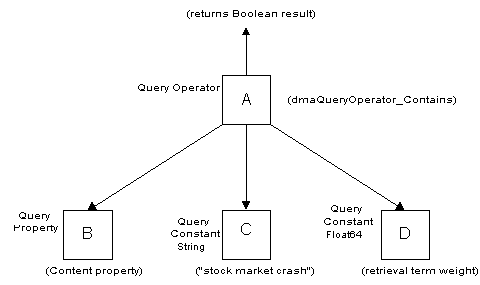
Fig. 1. Contains Operator Structure (click for
Visio).
The object A is of class Query Operator. The value of its Query Operator Id property is
dmaQueryOperator_Contains.
The objects B, C, and D are objects referenced by the values of Operands[0],
Operands[1], and Operands[2], respectively.
The object B is of class Query Property. The value of its Property Id property is
dmaProp_Content.
The object C is of class Query Constant string. The value of its Constant Value String
property is "stock market crash".
The object D is of class Query Constant Float64. The value of its Constant Value
Float64 property is 1.0.
Suppose the example query described in the previous section were to be executed, and 10
result items were generated. Further suppose that the only classes that were indexed in
the full text index were subclasses of DocVersion. Finally, suppose that the Result Object
property was included in the Selections list. Then, for each of the 10 result items,
accessing the value of the Result Objects property of the result item would result in the
creation of a scratch pad object. The scratch pad object would be connected to a DocVer
for a document stored in the document space that contains the phrase "stock market
crash" somewhere in its content. The connected scratch pad object could then be used
to access the properties and content of the document in the usual way.
Suppose you wanted to find documents that had the word "skydiving" and the
phrase "world championships" with no more than 9 words between the two search
terms. Suppose you didn’t care which order the two terms occurred in, and that the
relative importance of this retrieval term was 1.0. Then you could have the following
subtree in the query parse tree:
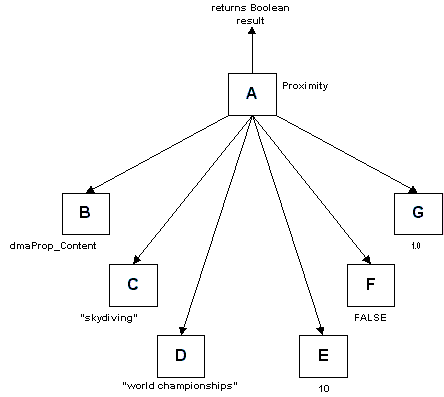
Fig. 2. Proximity Operator Structure (click
for Visio)
The objects B, C, D, E, F, and G are the referenced by Operands[0] throught
Operands[5], respectively. The value of Operands[3] is 10, not 9, because there are at
most 9 intervening words between the two search terms. The value of Operands[4] is FALSE,
because the order of the two search terms doesn’t matter.
This example illustrates how the logical operators (And, Or, and Not) can be used to
form compound query conditions. Suppose you wanted to find documents that contained either
the phrase "Andrew Johnson" or the word "impeachment" or both, and
that the relative importance of this retrieval term is 1.0. Note that there is no
requirement that the two search terms both occur in the document – either one would
be sufficient. Then you could have the following subtree in your query parse tree:
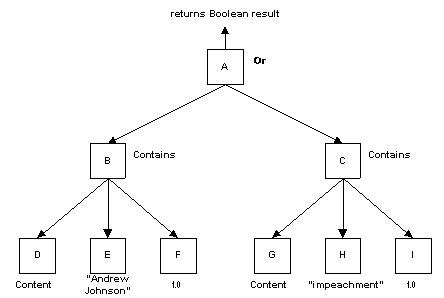
Fig. 3. Compound CBSearch Condition (click
for Visio)
Most of the new properties introduced to the Query class are Booleans. In order to
illustrate how to use the information they provide, it should be sufficient to consider
just one of them, say, CBR Soundex.
Several possibilities exist: (1) The content search engine does not do Soundex
searches. In this case, the CBR Soundex property, if implemented, would be read only, and
would have the value FALSE. (2) The content search only does Soundex searches, not
ordinary vocabulary based searches. In this case, the CBR Soundex property, if
implemented, would be read only, and have the value TRUE. (3) The content search engine
supports ordinary vocabulary based searched as well as Soundex. In this case, the CBR
Soundex property, if implemented, would be read-write. The default would be either TRUE or
FALSE, but FALSE is probably a better default.
By using the information about whether the CBR Soundex property is read only or
read-write (which it could get from the metadata of this property), the user interface
program could gray out the Soundex option or not, and show the default value. If
read-write, the user interface program could let the user override the default setting.
The user interface program would build the query parse tree according to the end
user’s instructions. The server software would look at the value of the CBR Soundex
property, and use the Soundex algorithm or not. Of course, if Soundex wasn’t
implemented, the server software could simply ignore the value of the CBR Soundex
property.
The proposal is additive. New classes, properties, and operators are added. Nothing is
deleted or modified.
This will allow existing systems to use content based retrieval with DMA. There is no
negative impact on them.
The entire feature is optional. The Content Search class and all the content search
query operators are optional. To provide the feature, at least pure content search queries
must be supported. A companion capabilities proposal specifies
the optional constraints on the query condition.
Content search is necessary to complete the basic functionality of DMA. Oracle Corp.
stated that they thought it was so important that it had to be included in release 1.0 of
the DMA API specification.
This is a good solution because it is simple and straightforward for document space
implementations to make their content based retrieval functionality available by defining
content based search operators on the Content Search class. In other words, it is a good
fit with existing implementations.
Another reason the solution is good is because it fits well with the existing query
model.
Most commercially available document management systems provide content based
retrieval, e.g., FileNET, Documentum, etc..
- Hitachi working paper: Content-based Retrieval Extension of DMA Query Model (dated July
20, 1998)
- Minutes of DMA Query subcommittee meeting for content search discussions
- Hitachi slide presentation of their content based retrieval proposal
- STARTS, Stanford Protocol Proposal for Internet Retrieval and Search. Last modified
January 19, 1997. Luis Gravano, Kevin Chang, Hector Garcia-molina, Carl Lagoze, Andreas
Paepcke. Digital Library Project, Stanford University.
- User manual for Mezzanine.
- User manual for Documentum.
The new classes and new properties must be added as per section 5 above.
The query model overview must be updated as per section 7.2.1 above.
New query operators must be added to the query operators table as per section 7.2.2 above.
html rendition derived 1999-08-06-00:13 -0700
(pdt)
$$Date: 00-02-17 15:07 $
$$Revision: 5 $


